ASP.NET Identity ベースのフォーム認証を実装した ASP.NET MVC5 アプリケーションで、管理者がロール管理を行う機能を実装する例を書きます。先の記事「ASP.NET Identity のユーザー管理 (MVC)」の続きです。
CodeZine の記事「ASP.NET Identityでユーザーに役割(ロール)を持たせる
」に、ASP.NET Web Forms アプリ用のユーザー管理画面を作る手順が載っていますが、その MVC 版です。
ベースとなるのは、先の記事「ASP.NET Identity のユーザー管理 (MVC)」と同様、Visual Studio 2015 Community で MVC のテンプレートを利用し、認証に「個別のユーザーアカウント」を指定して自動生成させたプロジェクトです。
それにロール情報の追加、変更、削除および登録済みユーザーのロールのアサインを行う機能を実装するには以下のようにします:
(1) コードの追加
ロール情報の追加、変更、削除を行うのに用いるクラスは、IdentityRole クラスと RoleManager<TRole, TKey> クラスです。
テンプレートで自動生成されたコードにはそれらのコードは含まれていませんので追記する必要があります。
具体的には、Models\IdentityModels.cs, App_Start\IdentityConfig.cs, App_Start\Startup.Auth.cs の 3 つの既存のファイルに、CodeZine の記事「ASP.NET Identityでユーザーに役割(ロール)を持たせる」を参考にコードを追加します。(記事のコードをそのままコピペすれば OK)
何を追加するかを簡単に書きますと、IdentityModels.cs, IdentityConfig.cs, Startup.Auth.cs の順に、以下の通りです。
-
IdentityRole クラスを継承した ApplicationRole クラスを IdentityModels.cs に追加。
-
RoleManager<TRole, TKey> クラスを継承した ApplicationRoleManager クラスを IdentityConfig.cs に追加。定義には ApplicationRoleManager クラスのインスタンスを生成して OwinContext に登録するための Create メソッドを含める。Create メソッドにはロールストアに何も定義されてない場合 Administrator という名前のロールを作成するコードも含まれています。
-
ApplicationRoleManager のインスタンスを生成して OwinContext に登録するコードを Startup.Auth.cs の ConfigureAuth メソッドに追加。これにより、Controller で HttpContext.GetOwinContext() メソッドにより OwinContext を取得し、それから Get<ApplicationRoleManager>() メソッドで ApplicationRolerManager オブジェクトを取得できるようになります。
(2) Migrations を実施
上記 (1) の作業後アプリを実行すると、先にユーザー情報を登録して EF Code First の機能で DB を生成済みの場合は以下のようなエラーが出ると思います。ちなみに、下の画像でエラーとなっている行は、上記 (1) - 2 で追加した Create メソッドでロールストアにあるロール情報を取得するものです。
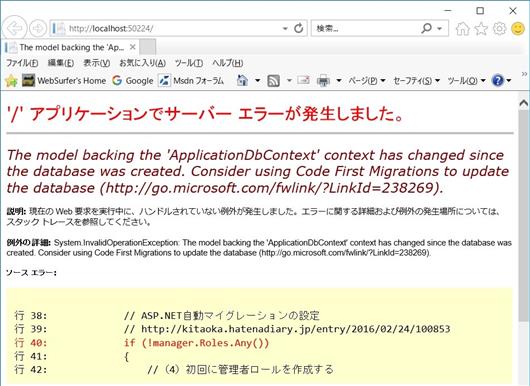
その場合は Migrations 実施してから再度実行してください。
具体的には、Visual Studio のパッケージマネージャーコンソールで、Enable-Migrations コマンドを実行して Code First Migrations を有効にし、次に Update-Database –Verbose コマンドを実行して保留中の移行をデータベースに適用します。
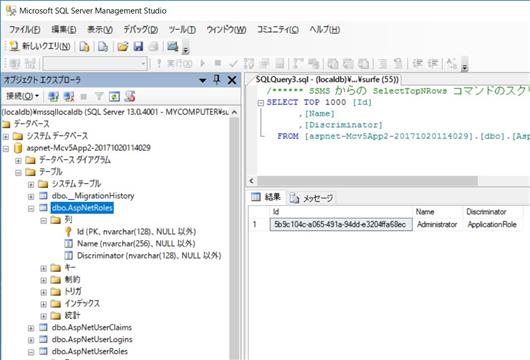
(3) AspNetRoles テーブルの確認
上記 (2) でエラーなく無事実行できれば、以下の画像のようにロール情報のストアとなる AspNetRoles テーブルに Discriminator フィールドが追加され、「結果」ウィンドウに示すように Name が Administrator というレコードができているはずです。
(4) ロール管理用 Controller / View の実装
ロール情報の追加、変更、削除および登録済みユーザーのロールのアサインを行うための Controller / View を実装します。Controller の実装例を以下に示します。説明はコード内のコメントに書きましたので、それを見てください。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Mvc;
// 上は自動生成されたもの。それに以下の名前空間を追加
using Microsoft.AspNet.Identity;
using Microsoft.AspNet.Identity.Owin;
using System.Net;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Mcv5App2.Models;
namespace Mcv5App2.Controllers
{
// 以下の RoleModel, UserWithRoleInfo, RoleInfo の 3 クラス
// はここで利用する Model。Controller 内に定義したのは単に
// 分けるのが面倒だから
// アクションメソッド Create, Edit 用の Model
public class RoleModel
{
[Required]
[StringLength(
100,
ErrorMessage = "{0} は {2} 文字以上",
MinimumLength = 3)]
[Display(Name = "Role")]
public string Role { get; set; }
}
// アクションメソッド UserWithRoles, EditRoleAssignment
// (各ユーザーのロール一覧表示、ロールのアサイン・削除)
// 用の Model
public class UserWithRoleInfo
{
public UserWithRoleInfo()
{
UserRoles = new List<RoleInfo>();
}
public string UserId { set; get; }
public string UserName { set; get; }
public string UserEmail { set; get; }
public IList<RoleInfo> UserRoles { set; get; }
}
public class RoleInfo
{
public string RoleName { set; get; }
public bool IsInThisRole { set; get; }
}
// ここから Controller のコード
public class RolesController : Controller
{
private ApplicationUserManager _userManager;
private ApplicationRoleManager _roleManager;
public ApplicationUserManager UserManager
{
get
{
return _userManager ??
HttpContext.GetOwinContext().
GetUserManager<ApplicationUserManager>();
}
private set
{
_userManager = value;
}
}
public ApplicationRoleManager RoleManager
{
get
{
return _roleManager ??
HttpContext.GetOwinContext().
Get<ApplicationRoleManager>();
}
private set
{
_roleManager = value;
}
}
// GET: Roles(登録済みロールの一覧)
// Model は ApplicationRole
public ActionResult Index()
{
var roles =
RoleManager.Roles.OrderBy(role => role.Name);
return View(roles);
}
// GET: Roles/Details/Id(指定 Id のロール詳細)
// 上の一覧以上の情報は含まれないので不要かも・・・
// Model は ApplicationRole
public async Task<ActionResult> Details(string id)
{
if (id == null)
{
return new HttpStatusCodeResult(
HttpStatusCode.BadRequest);
}
var target = await RoleManager.FindByIdAsync(id);
if (target == null)
{
return HttpNotFound();
}
return View(target);
}
// GET: Roles/Create(新規ロール作成・登録)
// Model は上に定義した RoleModel クラス
public ActionResult Create()
{
return View();
}
// POST: Roles/Create(新規ロール作成・登録)
// Model は上に定義した RoleModel クラス
[HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public async Task<ActionResult> Create(RoleModel model)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
// ユーザーが入力したロール名を model.Role から取得し
// て ApplicationRole を生成
var role = new ApplicationRole { Name = model.Role };
// 上の ApplicationRole から新規ロールを作成・登録
var result = await RoleManager.CreateAsync(role);
if (result.Succeeded)
{
// 登録に成功したら Roles/Index にリダイレクト
return RedirectToAction("Index", "Roles");
}
// result.Succeeded が false の場合 ModelSate にエ
// ラー情報を追加しないとエラーメッセージが出ない。
// AccountController と同様に AddErrors メソッドを
// 定義して利用(一番下に定義あり)
AddErrors(result);
}
// ロールの登録に失敗した場合、登録画面を再描画
return View(model);
}
// GET: Roles/Edit/Ed(指定 Id のロール情報の更新)
// ここで更新できるのはロール名のみ
// Model は上に定義した RoleModel クラス
public async Task<ActionResult> Edit(string id)
{
if (id == null)
{
return new HttpStatusCodeResult(
HttpStatusCode.BadRequest);
}
var target = await RoleManager.FindByIdAsync(id);
if (target == null)
{
return HttpNotFound();
}
RoleModel model = new RoleModel() { Role = target.Name };
return View(model);
}
// POST: Roles/Edit/Id(指定 Id のロール情報の更新)
// ここで更新できるのはロール名のみ
// Model は上に定義した RoleModel クラス
[HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public async Task<ActionResult>
Edit(string id, RoleModel model)
{
if (id == null)
{
return new HttpStatusCodeResult(
HttpStatusCode.BadRequest);
}
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
var target = await RoleManager.FindByIdAsync(id);
// ユーザーが入力したロール名を model.Role から取得し
// て ApplicationRole の Name を書き換え
target.Name = model.Role;
// Name を書き換えた ApplicationRole で更新をかける
var result = await RoleManager.UpdateAsync(target);
if (result.Succeeded)
{
// 更新に成功したら Roles/Index にリダイレクト
return RedirectToAction("Index", "Roles");
}
// result.Succeeded が false の場合 ModelSate にエ
// ラー情報を追加しないとエラーメッセージが出ない。
AddErrors(result);
}
// 更新に失敗した場合、編集画面を再描画
return View(model);
}
// GET: Roles/Delete/Id(指定 Id のロールを削除)
// 階層更新が行われているようで、ユーザーがアサインされて
// いるロールも削除可能。
// Model は ApplicationRole
public async Task<ActionResult> Delete(string id)
{
if (id == null)
{
return new HttpStatusCodeResult(
HttpStatusCode.BadRequest);
}
var target = await RoleManager.FindByIdAsync(id);
if (target == null)
{
return HttpNotFound();
}
return View(target);
}
// POST: Roles/Delete/Id(指定 Id のロールを削除)
// Model は ApplicationRole
// 上の Delete(string id) と同シグネチャのメソッド
// は定義できないので、メソッド名を変えて、下のよう
// に ActionName("Delete") を設定する
[HttpPost, ActionName("Delete")]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public async Task<ActionResult>
DeleteConfirmed(string id)
{
if (id == null)
{
return new HttpStatusCodeResult(
HttpStatusCode.BadRequest);
}
var target = await RoleManager.FindByIdAsync(id);
if (target == null)
{
return HttpNotFound();
}
// ユーザーがアサインされているロールも以下の一行で
// 削除可能。内部で階層更新が行われているらしい。
var result = await RoleManager.DeleteAsync(target);
if (result.Succeeded)
{
// 削除に成功したら Roles/Index にリダイレクト
return RedirectToAction("Index", "Roles");
}
// result.Succeeded が false の場合 ModelSate にエ
// ラー情報を追加しないとエラーメッセージが出ない。
AddErrors(result);
// 削除に失敗した場合、削除画面を再描画
return View(target);
}
// 以下は:
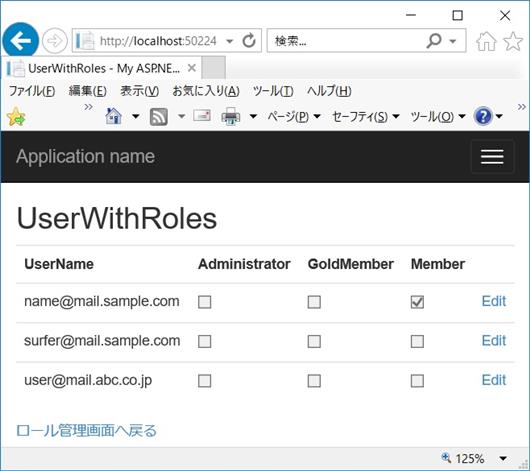
// (1) UserWithRoles で、上の画像のように、登録済みユーザー
// の一覧と各ユーザーへのロールのアサイン状況を表示し、
// (2) Edit ボタンクリックで EditRoleAssignment に遷移し、
// 当該ユーザーへのロールのアサインを編集して保存する
// ・・・ためのもの。
// GET: Roles/UserWithRoles
// ユーザー一覧と各ユーザーにアサインされているロールを表示
// Model は上に定義した UserWithRoleInfo クラス
public async Task<ActionResult> UserWithRoles()
{
var model = new List<UserWithRoleInfo>();
// ToList() を付与してここで DB からデータを取得して
// DataReader を閉じておかないと、下の IsInRole メソッド
// でエラーになるので注意
var users = UserManager.Users.
OrderBy(user => user.UserName).ToList();
var roles = RoleManager.Roles.
OrderBy(role => role.Name).ToList();
foreach (ApplicationUser user in users)
{
UserWithRoleInfo info = new UserWithRoleInfo();
info.UserId = user.Id;
info.UserName = user.UserName;
info.UserEmail = user.Email;
foreach (ApplicationRole role in roles)
{
RoleInfo roleInfo = new RoleInfo();
roleInfo.RoleName = role.Name;
roleInfo.IsInThisRole = await
UserManager.IsInRoleAsync(user.Id, role.Name);
info.UserRoles.Add(roleInfo);
}
model.Add(info);
}
return View(model);
}
// GET: Roles/EditRoleAssignment/Id
// 指定 Id のユーザーのロールへのアサインの編集
// Model は上に定義した UserWithRoleInfo クラス
public async Task<ActionResult>
EditRoleAssignment(string id)
{
if (id == null)
{
return new HttpStatusCodeResult(
HttpStatusCode.BadRequest);
}
var user = await UserManager.FindByIdAsync(id);
if (user == null)
{
return HttpNotFound();
}
UserWithRoleInfo model = new UserWithRoleInfo();
model.UserId = user.Id;
model.UserName = user.UserName;
model.UserEmail = user.Email;
// ToList() を付与しておかないと下の IsInRole メソッド
// で DataReader が閉じてないというエラーになる
var roles = RoleManager.Roles.
OrderBy(role => role.Name).ToList();
foreach (ApplicationRole role in roles)
{
RoleInfo roleInfo = new RoleInfo();
roleInfo.RoleName = role.Name;
roleInfo.IsInThisRole = await
UserManager.IsInRoleAsync(user.Id, role.Name);
model.UserRoles.Add(roleInfo);
}
return View(model);
}
// GET: Roles/EditRoleAssignment/Id
// 指定 Id のユーザーのロールへのアサインの編集
// Model は上に定義した UserWithRoleInfo クラス
[HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public async Task<ActionResult>
EditRoleAssignment(string id, UserWithRoleInfo model)
{
if (id == null)
{
return new HttpStatusCodeResult(
HttpStatusCode.BadRequest);
}
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
IdentityResult result;
foreach (RoleInfo roleInfo in model.UserRoles)
{
// id のユーザーが roleInfo.RoleName のロールに属して
// いるか否か。以下でその情報が必要。
bool isInRole = await
UserManager.IsInRoleAsync(id, roleInfo.RoleName);
// roleInfo.IsInThisRole には編集画面でロールのチェッ
// クボックスのチェック結果が格納されている
if (roleInfo.IsInThisRole)
{
// チェックが入っていた場合
// 既にロールにアサイン済みのユーザーを AddToRole
// するとエラーになるので以下の判定が必要
if (isInRole == false)
{
result = await UserManager.
AddToRoleAsync(id, roleInfo.RoleName);
if (!result.Succeeded)
{
AddErrors(result);
return View(model);
}
}
}
else
{
// チェックが入っていなかった場合
// ロールにアサインされてないユーザーを
// RemoveFromRole するとエラーになるので以下の
// 判定が必要
if (isInRole == true)
{
result = await UserManager.
RemoveFromRoleAsync(id, roleInfo.RoleName);
if (!result.Succeeded)
{
AddErrors(result);
return View(model);
}
}
}
}
// 編集に成功したら Roles/UserWithRoles にリダイレクト
return RedirectToAction("UserWithRoles", "Roles");
}
// 編集に失敗した場合、編集画面を再描画
return View(model);
}
protected override void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
if (disposing)
{
if (_userManager != null)
{
_userManager.Dispose();
_userManager = null;
}
if (_roleManager != null)
{
_roleManager.Dispose();
_roleManager = null;
}
}
base.Dispose(disposing);
}
// ModelSate にエラー情報を追加するためのヘルパメソッド
private void AddErrors(IdentityResult result)
{
foreach (var error in result.Errors)
{
ModelState.AddModelError("", error);
}
}
}
}
MSDN ライブラリの UserManager<TUser> クラス、RoleManager<TRole, TKey> クラスの説明には非同期版メソッドしか書いてないのでそれらを使っていますが、同期版も拡張メソッドとして定義されているようです。ケースバイケースでどちらが適切かを考えて使い分けた方が良いかもしれません。
View はコントローラをベースにスキャフォールディング機能を利用して自動生成できます。Visual Studio でアクションメソッドのコードを右クリックして[ビューを追加(D)...]を選ぶと、そのためのダイアログが表示されます。
アクションメソッド EditRoleAssignment に対応する View は自動生成されるコードだけでは不十分でいろいろ追加・修正が必要です。以下にその完成版のコードを載せておきます。
@model Mcv5App2.Controllers.UserWithRoleInfo
@{
ViewBag.Title = "EditRoleAssignment";
Layout = "~/Views/Shared/_Layout.cshtml";
}
<h2>EditRoleAssignment</h2>
@using (Html.BeginForm())
{
@Html.AntiForgeryToken()
<h4>UserWithRoleInfo</h4>
<hr />
@Html.ValidationSummary("",new { @class="text-danger" })
<table class="table">
<tr>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.UserName)
</th>
@foreach (var role in Model.UserRoles)
{
<th>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => role.RoleName)
</th>
}
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.UserName)
@Html.HiddenFor(model => model.UserName)
@Html.HiddenFor(model => model.UserEmail)
@Html.HiddenFor(model => model.UserId)
</td>
@for (int i = 0; i < Model.UserRoles.Count; i++)
{
<td>
@Html.EditorFor(model =>
model.UserRoles[i].IsInThisRole)
@Html.HiddenFor(model =>
model.UserRoles[i].RoleName)
</td>
}
</tr>
</table>
<div class="form-group">
<div class="col-md-offset-2 col-md-10">
<input type="submit" value="Save"
class="btn btn-default" />
</div>
</div>
}
<div>
@Html.ActionLink("Back to List", "UserWithRoles")
</div>
@section Scripts {
@Scripts.Render("~/bundles/jqueryval")
}
上の View のコードで注意すべき点は、コレクション(上の例では Model.UserRoles で取得できる RoleInfo クラスのコレクション) についてはレンダリングされる html 要素の name 属性が連番のインデックスを含むようにすることです。具体的には、name="prefix[index].Property" というパターンにします。
そうしないとモデルバインディングがうまくいきません。その理由など詳しくは先の記事「コレクションのデータアノテーション検証」を見てください。