by WebSurfer
2021年1月17日 17:41
ファイルをアップロード/ダウンロードする相手が ASP.NET Core 3.1 Web API の場合はどのようにすれば良いかについて書きます。
コードを書いてみましたが、先の記事「ASP.NET Core 3.1 Web API」に書いた、(1) Controller は ControllerBase クラスを継承、(2) ApiControllerAttribute 属性を付与、(3) ルーティングは RouteAttibute 属性を付与して設定、アクションメソッドに [HttpGet], [HttpPost] 属性を付与する以外は MVC の場合とほとんど変わりませんでした。
(MVC の場合は、先の記事「ASP.NET Core MVC でファイルアップロード」と「ASP.NET Core MVC でファイルダウンロード」を見てください)
それでこの記事の話は終わってしまうのですが、それではちょっとブログの記事としては寂しいし、今後の参考になるかもしれないので検証に使ったコードを下にアップしておきます。
Web API コントローラー/アクションメソッド
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using System.IO;
namespace WebAPI.Controllers
{
[ApiController]
[Route("[controller]")]
public class FileUpDownloadController : ControllerBase
{
// 物理パスの取得用
private readonly IWebHostEnvironment _hostingEnvironment;
public FileUpDownloadController(IWebHostEnvironment hostingEnvironment)
{
this._hostingEnvironment = hostingEnvironment;
}
[HttpPost]
public async Task<IActionResult> PostFile(IFormFile postedFile)
{
string result = "";
if (postedFile != null && postedFile.Length > 0)
{
// アップロードされたファイル名を取得。ブラウザが IE
// の場合 postedFile.FileName はクライアント側でのフ
// ルパスになることがあるので Path.GetFileName を使う
string filename = Path.GetFileName(postedFile.FileName);
// アプリケーションルートの物理パスを取得
// wwwroot の物理パスは WebRootPath プロパティを使う
string contentRootPath = _hostingEnvironment.ContentRootPath;
string filePath = contentRootPath + "\\" +
"UploadedFiles\\" + filename;
using (var stream = new FileStream(filePath, FileMode.Create))
{
await postedFile.CopyToAsync(stream);
}
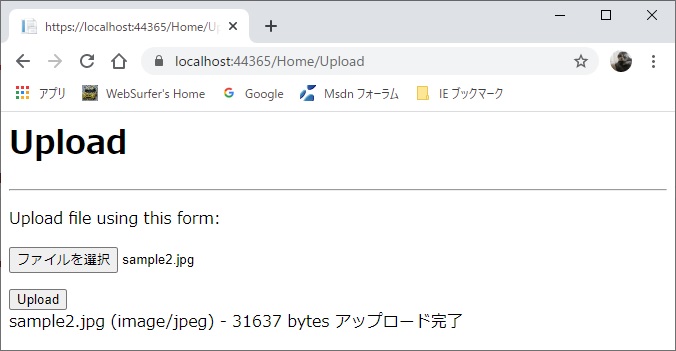
result = filename + " (" + postedFile.ContentType +
") - " + postedFile.Length +
" bytes アップロード完了";
}
else
{
result = "ファイルアップロードに失敗しました";
}
return Content(result);
}
[HttpGet]
[ResponseCache(Duration = 0,
Location = ResponseCacheLocation.None, NoStore = true)]
public IActionResult GetFile(string filename = "sample1.jpg")
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(filename))
{
return NotFound("引数が null または空");
}
// アプリケーションルートの物理パスを取得
string contentRootPath = _hostingEnvironment.ContentRootPath;
// ダウンロードするファイルの物理パス
string physicalPath = contentRootPath + "\\" +
"Files\\" + filename;
if (!System.IO.File.Exists(physicalPath))
{
return NotFound("指定されたパスにファイルが無い");
}
// Content-Disposition ヘッダを設定(RFC 6266 対応してない)
Response.Headers.Append("Content-Disposition",
"attachment;filename="+filename);
return new PhysicalFileResult(physicalPath, "image/jpeg");
}
}
}
アップロードの検証に使った View
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Upload";
}
<h1>Upload</h1>
<hr />
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-4">
<form method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<div>
<div>
<p>Upload file using this form:</p>
@* name 属性はモデルのクラスのプロパティ名と同じ
にしないとサーバー側でモデルバインディングさ
れないので注意。大文字小文字は区別しない。*@
<input type="file" name="postedfile" />
</div>
</div>
</form>
<div>
<div>
<input type="button" id="ajaxUpload" value="Upload" />
<div id="result"></div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script src="~/Scripts/jquery.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
//<![CDATA[
$(function () {
$('#ajaxUpload').on('click', function (e) {
// FormData オブジェクトの利用
var fd = new FormData(document.querySelector("form"));
$.ajax({
url: '/FileUpDownload',
method: 'post',
data: fd,
processData: false, // jQuery にデータを処理させない
contentType: false // contentType を設定させない
}).done(function(response) {
$("#result").empty;
$("#result").text(response);
}).fail(function( jqXHR, textStatus, errorThrown ) {
$("#result").empty;
$("#result").text('textStatus: ' + textStatus +
', errorThrown: ' + errorThrown);
});
});
});
//]]>
</script>
ダウンロードの検証はブラウザのアドレスバーにコントローラーの URL を入力して FileUpDownload を GET 要求すれば可能です。ファイル名はデフォルトで "sample1.jpg" となっていますが、クエリ文字列で別のファイルを指定できます。