ASP.NET Core Identity によるユーザー認証に用いるデータソースとプロバイダを独自実装する話を書きます。認証機能の全てを独自実装するわけではありません(そんな実力は自分にはありません)。具体的には、下の画像(Microsoft のドキュメントより借用)にある Data Source, Data Access Layer, Identity Store を自力で実装するだけです。
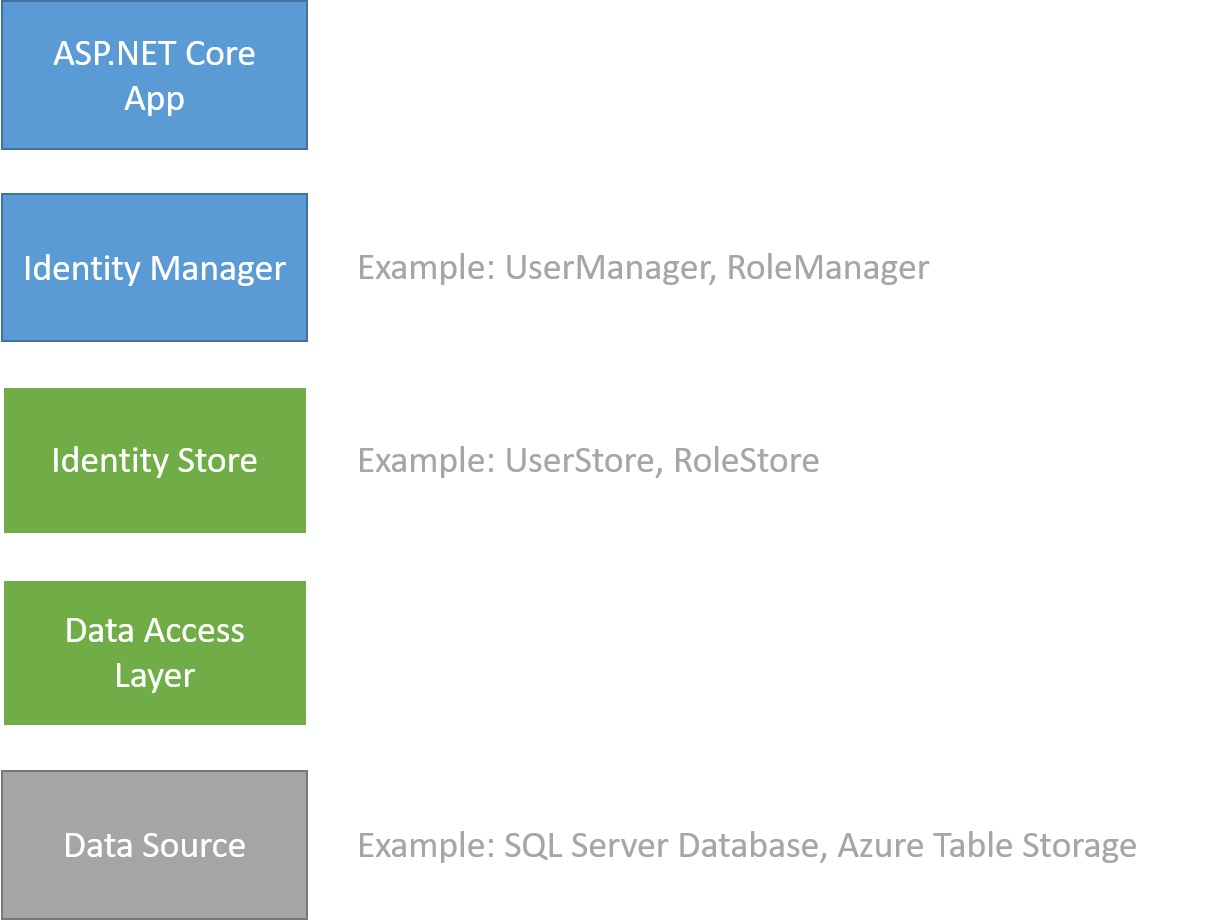
この記事のタイトルが「その1」となっているのは、まずはロール機能なしでユーザー認証を実装して「その1」として書き、ロール機能の追加を「その2」で書く予定だからです。(「その2」は途中で挫折するかもしれませんが・・・)
Data Source はユーザー名とパスワードだけを保持する SQL Server とし、Data Access Layer には Entity Framework を用い、Identity Store(プロバイダ)を独自実装して、Register, Login, Logout という基本機能を ASP.NET Core 3.1 MVC アプリで使えるようにしてみました。(アカウントロックアウト、メールを使ったアカウント確認とパスワードリセット、二要素認証などの機能は実装しません)
やってみて思ったのは、既存のデータベースにユーザー情報があってそれをどうしても使わなければならないということでなければ、独自実装を行うのに必要な時間と労力に見合うメリットはなさそうということです。(Visual Studio のテンプレートで「個別のユーザーアカウント」を選んでプロジェクトを生成すれば済むはずですので)
ということで、この記事の情報はあまり役に立たないかもしれませんが、せっかく実装して動くようになったので備忘録として書いておきます。
基本的なことは Mcrosoft のドキュメント Custom storage providers for ASP.NET Core Identity が参考になると思います。それに、"To create a custom storage provider, create the data source, the data access layer, and the store classes that interact with this data access layer (上の画像の緑色と灰色の箱). You don't need to customize the managers or your app code that interacts with them (上の画像の青色の箱)." と書いてあり、それに従いました。
クラスやメソッドのコードなど具体的な実装方法は Using your own database schema and classes with ASP.NET Core Identity and Entity Framework Core と Customize ASP.NET Core Identity を参考にさせていただきました。
それらの記事をベースに、上の画像の緑色と灰色の箱の部分を自力で実装した手順を以下に書きます。
(1) プロジェクトの作成
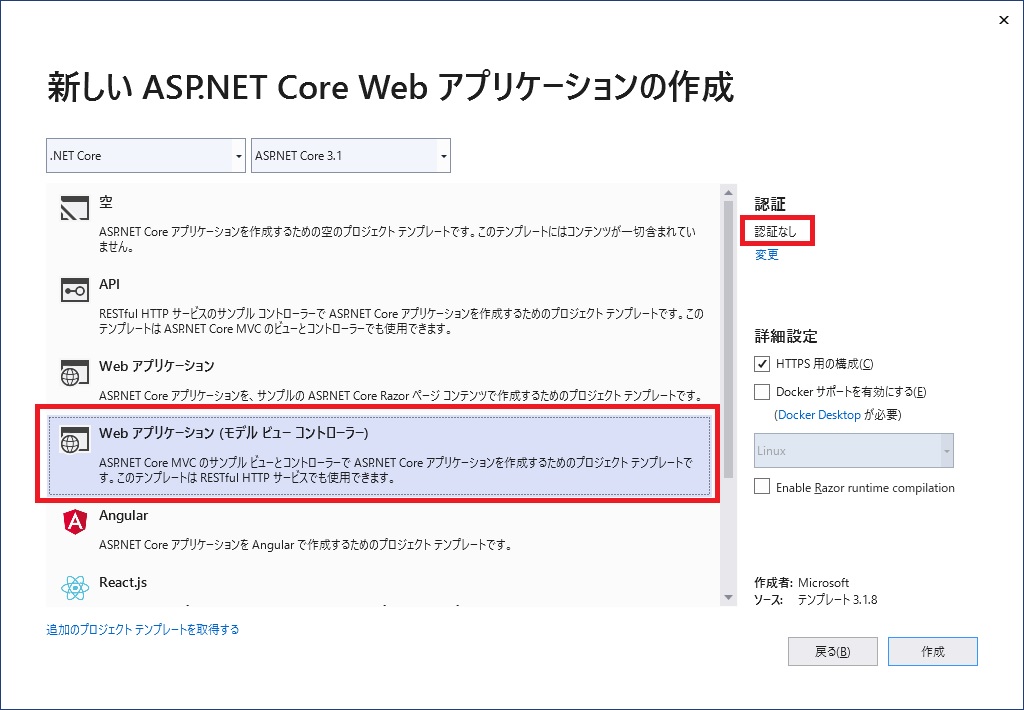
Visual Studio 2019 で Core 3.1 ベースの ASP.NET MVC アプリを認証なしで作成します。プロジェクト名は MvcIdCustom としました。(プロジェクト名は任意です)
(2) NuGet パッケージ
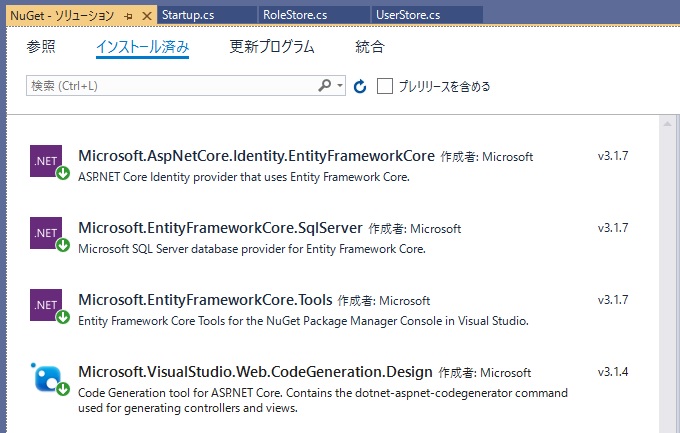
NuGet パッケージをインストールします。画像の上から 3 つは必須��ようです。一番下のパッケージは Visual Studio で Controller / View を生成する場合に必要なもので、ASP.NET Identity とは直接関係なさそうです。
(3) コンテキストクラスの実装
プロジェクトに DAL フォルダを新規に作ってそこにコンテキストクラス DataContext.cs を実装します。フォルダの名前やクラス名は任意ですが、これを使うコードで名前空間の指定などに影響しますので注意してください。
using MvcIdCustom.Models;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace MvcIdCustom.DAL
{
public class DataContext : DbContext
{
public DataContext(DbContextOptions<DataContext> options) :
base(options)
{
}
public DbSet<Role> Roles { get; set; }
public DbSet<User> Users { get; set; }
public DbSet<UserRole> UserRoles { get; set; }
}
}
(4) エンティティクラスの実装
既存の Models フォルダにエンティティクラス User, Role, UserRole を実装します。場所は Models フォルダでなくても良いですが、これを使うコードで名前空間の指定などに影響しますので注意してください。
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;
namespace MvcIdCustom.Models
{
[Table("User")]
public class User
{
[Key, Required]
public int Id { get; set; }
[Required, MaxLength(128)]
public string UserName { get; set; }
[Required, MaxLength(1024)]
public string PasswordHash { get; set; }
public virtual ICollection<UserRole> UserRoles { get; set; }
}
[Table("Role")]
public class Role
{
[Key, Required]
public int Id { get; set; }
[Required]
public string Name { get; set; }
public virtual ICollection<UserRole> UserRoles { get; set; }
}
[Table("UserRole")]
public class UserRole
{
[Key, Required]
public int Id { get; set; }
[Required, ForeignKey(nameof(User))]
public int UserId { get; set; }
[Required, ForeignKey(nameof(Role))]
public int RoleId { get; set; }
public virtual Role Role { get; set; }
public virtual User User { get; set; }
}
}
User クラスは「個別のユーザーアカウント」を選んでプロジェクトを生成した場合に使われる IdentityUser クラスに該当します。
(5) service と接続文字列の追加
上のコンテキストクラスとエンティティクラスをベースに、Entity Framework Code First の機能を利用して SQL Server に DB を生成するのですが、その前に以下の設定をしておきます。
i) Startup.cs に service を追加
以下のコードを Startup.cs 内の ConfigureServices メソッドに追加します。接続文字列名は任意です。この記事では "Default" としています。
services.AddDbContext<DataContext>(options =>
options.UseSqlServer(
Configuration.GetConnectionString("Default")));
ii) 接続文字列を appsettings.json に追加
プロジェクトに appsettings.json ファイルがあるので、
それを開いて以下のように接続文字列を追加します。
カンマ等必要に応じて追加して全体的に有効な JSON 形式となるよう注意してください。
"ConnectionStrings": {
"Default": "Server=(local)\\sqlexpress;Database=MvcIdCustom ..."
}
(6) Add-Migration, Update-Database
Visual Studio のパッケージマネージャーコンソールから Add-Migration CustomUserData コマンド(名前 CustomUserData は任意)を実行します。成功するとプロジェクトに Migrations フォルダと、その中に xxx_CustomUserData.cs ファイルが作られるはずです (xxx はコマンドの実行日時)。
その後 Update-Database を実行すれば、接続文字列に指定した名前(上の例では MvcIdCustom)で DB が生成され、その中にエンティティクラスの Table 属性に指定した名前のテーブルが生成されているはずです。
ここまでで、この記事の一番上の画像の Data Source と Data Access Layer の実装が終わったことになります。次はその上の Identity Store レイヤーの中の UserStore クラスの実装です。
(7) UserStore クラスの実装
参考にした記事をベースに、プロジェクトの DAL フォルダに、UserStore.cs として以下のように実装しました。この上のレイヤーにある UserManager, SignInManager がこのクラスに定義したメソッドを使って動くようです。
実装しましたとか簡単に書きましたが、上位レイヤーと調和を取って動くようにするにはどのように実装すべきかが全く分からず、実はこの実装が一番難問でした。パスワードのハッシュなど行われますが、何処でどう動いているのかさっぱり分かっていません。
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using MvcIdCustom.Models;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MvcIdCustom.DAL
{
public class UserStore : IUserStore<User>,
IUserPasswordStore<User>,
IQueryableUserStore<User>
{
private DataContext db;
public UserStore(DataContext db)
{
this.db = db;
}
public void Dispose()
{
Dispose(true);
}
protected virtual void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
if (disposing)
{
if (db != null)
{
db.Dispose();
db = null;
}
}
}
// IQueryableUserStore<User> のメンバー
public IQueryable<User> Users
{
get { return db.Users.Select(u => u); }
}
// IUserStore<TUser>
public Task<string> GetUserIdAsync(User user,
CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
cancellationToken.ThrowIfCancellationRequested();
if (user == null) throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(user));
return Task.FromResult(user.Id.ToString());
}
// IUserStore<TUser>
public Task<string> GetUserNameAsync(User user,
CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
cancellationToken.ThrowIfCancellationRequested();
if (user == null) throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(user));
return Task.FromResult(user.UserName);
}
// IUserStore<TUser>
public Task SetUserNameAsync(User user,
string userName,
CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
cancellationToken.ThrowIfCancellationRequested();
if (user == null) throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(user));
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(userName))
throw new ArgumentException("userName");
user.UserName = userName;
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
// IUserStore<TUser>
public Task<string> GetNormalizedUserNameAsync(User user,
CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
cancellationToken.ThrowIfCancellationRequested();
if (user == null) throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(user));
return Task.FromResult(user.UserName);
}
// IUserStore<TUser>
public Task SetNormalizedUserNameAsync(User user,
string normalizedName,
CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
cancellationToken.ThrowIfCancellationRequested();
if (user == null) throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(user));
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(normalizedName))
throw new ArgumentException("normalizedName");
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
// IUserStore<TUser>
// 同じユーザー名の二重登録の防止機能は上位レイヤーに組み込まれている
public async Task<IdentityResult> CreateAsync(User user,
CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
cancellationToken.ThrowIfCancellationRequested();
if (user == null) throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(user));
db.Add(user);
int rows = await db.SaveChangesAsync(cancellationToken);
if (rows > 0)
{
return IdentityResult.Success;
}
return IdentityResult.Failed(
new IdentityError { Description = $"{user.UserName} 登録失敗" });
}
// IUserStore<TUser>
// 同じユーザー名の二重登録の防止機能は上位レイヤーに組み込まれている
public async Task<IdentityResult> UpdateAsync(User user,
CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
cancellationToken.ThrowIfCancellationRequested();
if (user == null) throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(user));
db.Update(user);
int rows = await db.SaveChangesAsync(cancellationToken);
if (rows > 0)
{
return IdentityResult.Success;
}
return IdentityResult.Failed(
new IdentityError { Description = $"{user.UserName} 更新失敗" });
}
// IUserStore<TUser>
public async Task<IdentityResult> DeleteAsync(User user,
CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
cancellationToken.ThrowIfCancellationRequested();
if (user == null) throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(user));
db.Remove(user);
int rows = await db.SaveChangesAsync(cancellationToken);
if (rows > 0)
{
return IdentityResult.Success;
}
return IdentityResult.Failed(
new IdentityError { Description = $"{user.UserName} 削除失敗" });
}
// IUserStore<TUser>
public async Task<User> FindByIdAsync(string userId,
CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
cancellationToken.ThrowIfCancellationRequested();
if (int.TryParse(userId, out int id))
{
return await db.Users.SingleOrDefaultAsync(u => u.Id == id,
cancellationToken);
}
else
{
return await Task.FromResult<User>(null);
}
}
// IUserStore<TUser>
public async Task<User> FindByNameAsync(string normalizedUserName,
CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
cancellationToken.ThrowIfCancellationRequested();
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(normalizedUserName))
throw new ArgumentException("normalizedUserName");
User user = await db.Users.SingleOrDefaultAsync(
u => u.UserName.Equals(normalizedUserName.ToLower()),
cancellationToken);
return user;
}
// IUserPasswordStore<TUser>
public Task SetPasswordHashAsync(User user,
string passwordHash,
CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
cancellationToken.ThrowIfCancellationRequested();
if (user == null) throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(user));
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(passwordHash))
throw new ArgumentException("passwordHash");
user.PasswordHash = passwordHash;
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
// IUserPasswordStore<TUser>
public Task<string> GetPasswordHashAsync(User user,
CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
cancellationToken.ThrowIfCancellationRequested();
if (user == null) throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(user));
return Task.FromResult(user.PasswordHash);
}
// IUserPasswordStore<TUser>
public Task<bool> HasPasswordAsync(User user,
CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
cancellationToken.ThrowIfCancellationRequested();
if (user == null) throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(user));
return Task.FromResult(
!string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(user.PasswordHash));
}
}
}
ロール機能を使えるようにするには IUserRoleStore<User> を継承し、AddToRoleAsync, GetRolesAsync, IsInRoleAsync, RemoveFromRoleAsync メソッドを実装する必要があるかもしれませんが、それは「その2」で考えることにします。
(8) RoleStore クラスの実装
この記事「その1」ではロール機能は実装しないので必要ないのですが、「その2」で実装する予定ですので骨組みだけ作っておくことにしました。
using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using MvcIdCustom.Models;
namespace MvcIdCustom.DAL
{
public class RoleStore : IRoleStore<Role>, IQueryableRoleStore<Role>
{
public IQueryable<Role> Roles => throw new NotImplementedException();
public Task<IdentityResult> CreateAsync(Role role, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
public Task<IdentityResult> DeleteAsync(Role role, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
public void Dispose()
{
//throw new NotImplementedException();
}
public Task<Role> FindByIdAsync(string roleId, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
public Task<Role> FindByNameAsync(string normalizedRoleName, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
public Task<string> GetNormalizedRoleNameAsync(Role role, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
public Task<string> GetRoleIdAsync(Role role, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
public Task<string> GetRoleNameAsync(Role role, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
public Task SetNormalizedRoleNameAsync(Role role, string normalizedName, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
public Task SetRoleNameAsync(Role role, string roleName, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
public Task<IdentityResult> UpdateAsync(Role role, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
}
}
上の RoleStore クラスの中身は Visual Studio で自動生成できます。Dispose メソッドの throw new NotImplementedException(); をコメントアウトしておかないとエラーになるので注意してください。
(9) Startup.cs への追加
以下のコードを Startup.cs 内の ConfigureServices メソッドに追加します。
// Tell identity to use custom classes for users and roles
services.AddIdentity<User, Role>()
.AddDefaultTokenProviders();
// Tell identity to use custom storage provider for users
services.AddTransient<IUserStore<User>, UserStore>();
// Tell identity to use custom storage provider for roles
services.AddTransient<IRoleStore<Role>, RoleStore>();
さらに、認証ミドルウェアを使うために app.UseAuthorization(); を Configure メソッドに追加します。順番があるので注意してください。以下の場所に追加します。
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
// ・・・中略・・・
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
// 以下の一行を追加
app.UseAuthentication();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapControllerRoute(
name: "default",
pattern: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}");
});
}
以上でこの記事の一番上の画像の Data Source, Data Access Layer, Identity Store レイヤーの実装は完了です。ここまでの実装で、先の記事「ASP.NET Identity のユーザー管理 (CORE)」と同じ手段でユーザー情報の表示、追加、変更、削除が可能になることは確認しました。
次は Register, Login, Logout 機能の実装ですが、それを続けてここに書くと一つの記事としては長くなりすぎるので、別の記事「Register, Login, Logout 機能の実装」に書きました。
「その2」も書きました。こちらの記事「ASP.NET Core Identity 独自実装(その2)」です。